Digital Fashion — Clothes that aren’t there
Sitting in a cozy café in your favorite t-shirt, with one click you change into a shirt and put on a jacket. You can start a conference with your future client. Such perspective is becoming more and more real, and closer than ever, due to concept of Digital Fashion.

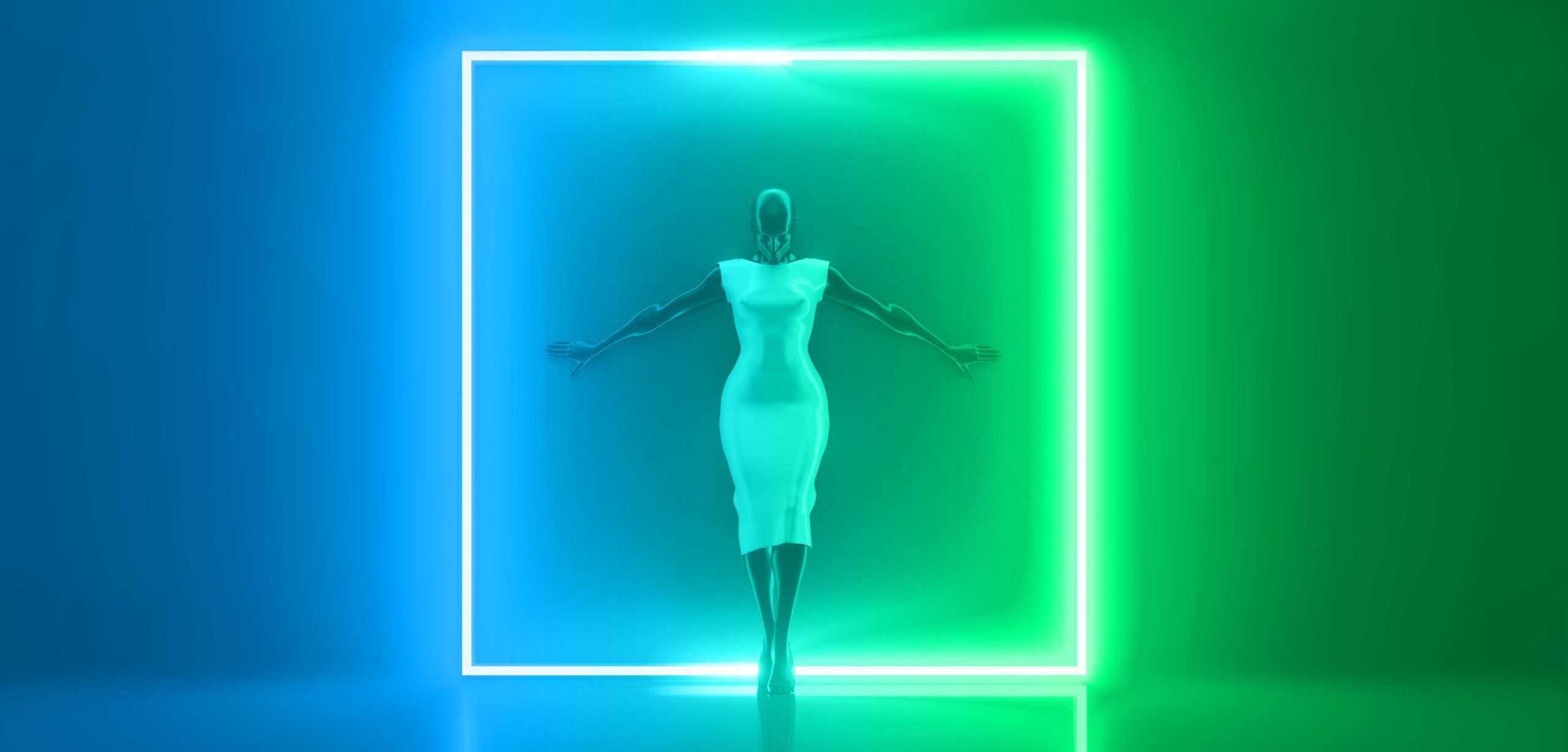
Pic. 1. Source
With the development of new technologies, especially 3D graphics (rendering, 3D models and fabric physics), the term is becoming increasingly popular. And what is Digital Fashion really? It is simply digital clothing – a virtual representation of clothing created using 3D software and then „superimposed” on a virtual human model.

Gif. 1. The Fabricant
Digital Fashion seems to be the next step in the development of the powerful e-commerce and fashion markets. Online stores started with descriptions and photos; now 360° product animations have become the norm, and digitally created models’ faces and bodies are increasingly being used for promotional graphics. The time for virtual fitting rooms and maybe even our own virtual wardrobes is coming. Actually, this (r)evolution has already taken its first steps. Let us just look at AR app projects of brands such as Nike (2019) or the collaboration of Italian fashion house Gucci with Snapchat (2020).

Gif. 2. Application for virtual shoe fitting. Source
Where did the need for this type of solution come from? The main, but not the only, factors giving rise to this type of application are:
On-line work and social relations – more and more events are moving or taking place simultaneously in the virtual world. The same applies to professions and even social gatherings. Remote working „via webcam” is no longer the domain of the IT industry, but increasingly appears in the entire sectors of the economy.
Environmental consciousness — digital clothes and accessories do not require farmland or animal husbandry for fabric and leather, as well as 93 billion cubic meters of water to produce textiles, laundry detergents, or global distribution routes. Designed once anywhere in the world, they can be globally available in no time.
The rapid increase in the popularity of items that do not exist in the real world – NFTs (non-fungible tokens) and people adopting digital alter egos.
The new generations are natives of technology. They largely communicate, and thus express themselves, in the virtual world. A perfect example of this trend is the success of fashion house Balenciaga’s campaign done in cooperation with the game Fortnite. Digital-to-Physical Partnerships will become more and more common.
Above, I have only outlined the emerging niche of Digital Fashion. It is also worth mentioning Polish achievements in this field – those interested may refer to the VOGUE article on the Nueno digital clothing brand and the article on homodigital.pl. Personally, I am extremely curious what virtual reality will bring to the e-commerce and fashion market in the coming years.

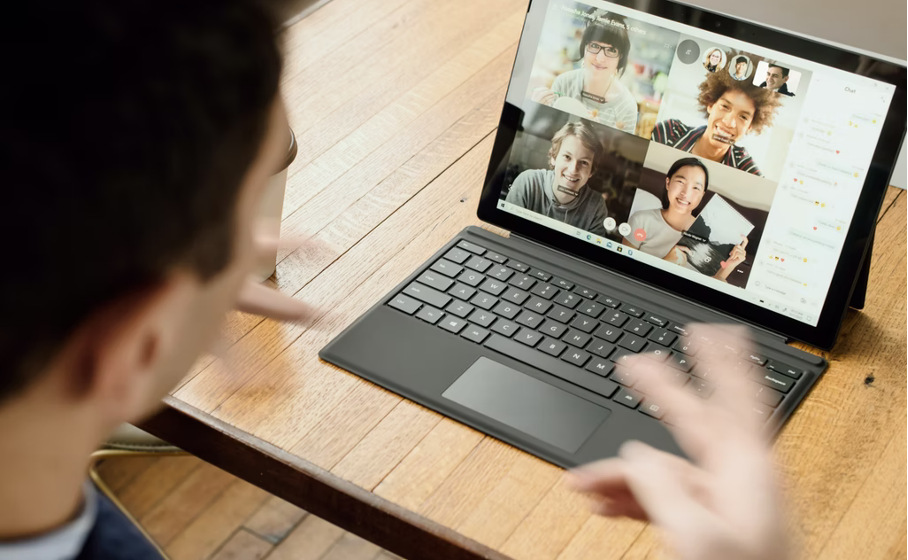
Pic.2. Digital Clothes made by STEPHY FUNG.
VR/DF Application — Big Picture
The rapid development of the Digital Fashion niche observed in recent years gives us huge, still largely undiscovered opportunities for the development of new products and services in this area. From designers specializing only in Digital Fashion, through professionals selecting textures for virtual fabrics, to programmers responsible for the unique physics of clothes. Personally, my favorite option would probably be to turn off gravity – you are sitting safely in a chair, and the shirt you’re wearing is acting like you’re in outer space. So naturally, space is created for apps that showcase emerging products and for marketplaces where customers will be able to view and purchase them.
For the purpose of this article, we will take on the challenge of creating just such a solution – an AR app connected to a digital clothing marketplace. The application will give the user the to create their own virtual styling, and clothing brands, as well as related brands, to officially sell their products and NFT.
Basic application principles
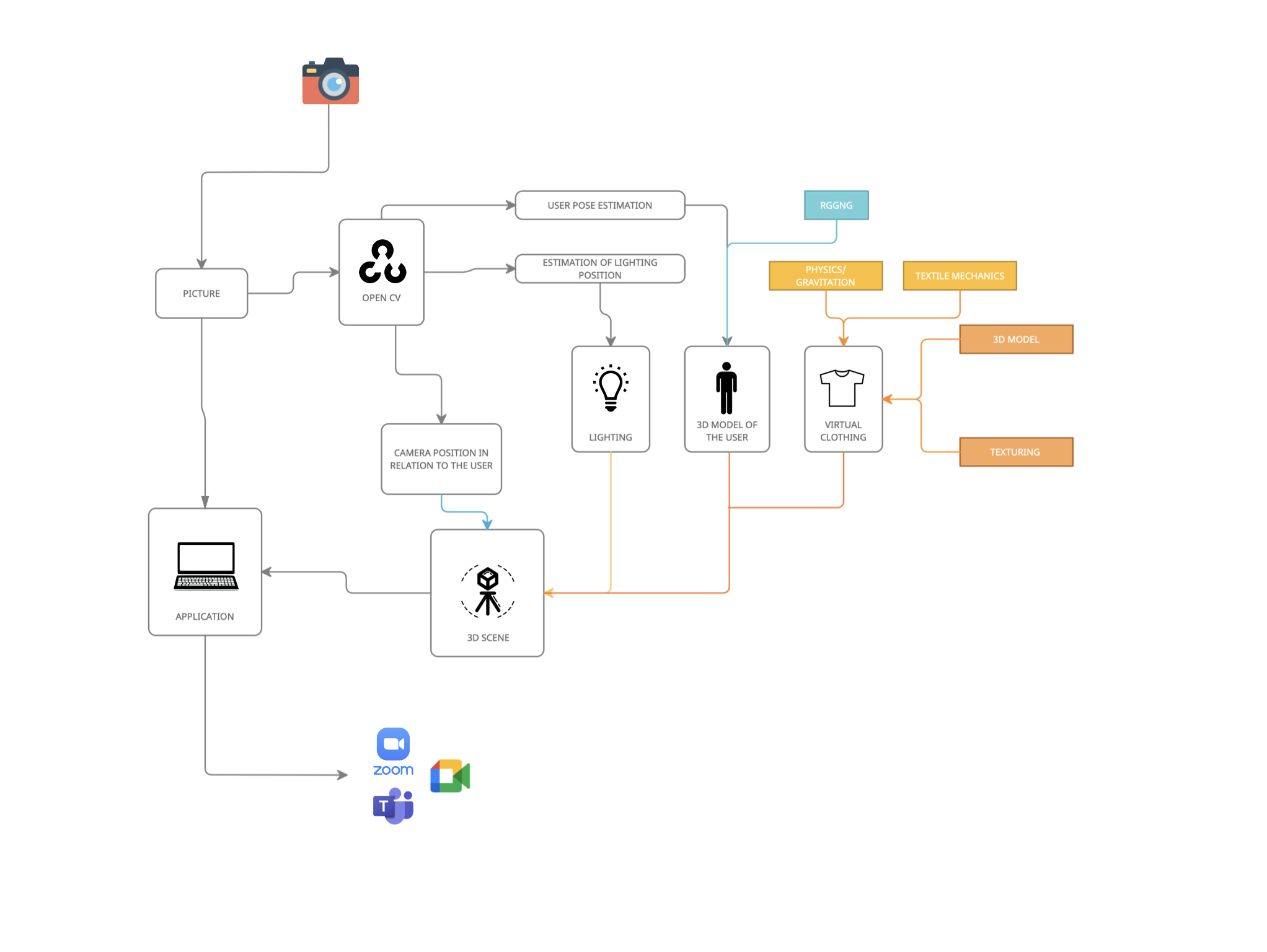
In theory, the operation is very simple – the application collects data about the user’s posture from the camera image, then processes it in real time using a library for human pose estimation (technology: OpenCV + Python). The collected data is actually just points in 3D space. They are transferred to the 3D engine, in which a virtual model of the User is created. The 3D model of the character itself is invisible, but interacts with visible clothes and/or accessories (technology: Blender 3D + Python). Ultimately, the user sees himself with the digital clothing superimposed.
Pic. 3. Diagram of the components of the application responsible for the virtual scene.
At this point, it is worth clarifying two terms:
POSE ESTIMATION — pose estimation is a computer vision technique that predicts movements and tracks the location of a person. We can also think of pose estimation as the problem of determining the position and orientation of a camera relative to an object. This is usually done by identifying, locating and tracking a number of key points on a person, such as the wrist, elbow or knee.
RIGGING — (skeletal animation) means equipping a 3D model of a human, animal or other character with jointed limbs and virtual bones.These form a skeleton inside the model, which makes it much easier and more efficient for the animator to maneuver – movements of the bones affect the movement of the 3D model.
The exchange of information between the program making the pose estimation and the skeleton inside the human model is the basis of the created application. Data packets about the position of characteristic points on the body, which are x, y, z parameters in space, will be connected with the same points in rigging of the 3D model of the figure.
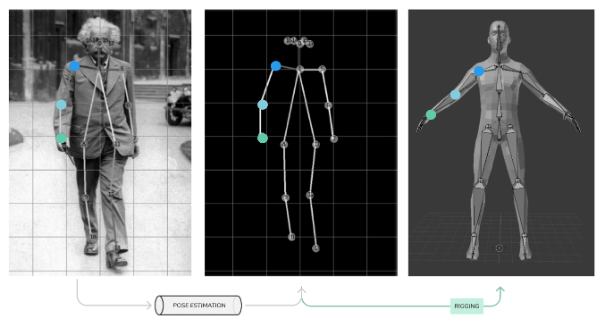 Pic. 4. Overlaying points from pose estimation on the joints of a 3D human model.
Pic. 4. Overlaying points from pose estimation on the joints of a 3D human model.
General guidelines for business objectives
The proposed solution does not go in the direction of a virtual avatar (i.e. it does not position itself as a replacement for a person’s image). We are interested in the environment around the person, in the surroundings – clothes, accessories, interiors, etc. – what is around is already a product. Following the proverb „closer to the body than the shirt”, the closest and always fashionable product are clothes – hence we will strongly focus on this segment of the market.
The question arises – what if the user wants to change their eye color? From there it’s close to swapping your hand for that of the Terminator after the fight in the final scene. I identify such needs as very interesting (e.g. in Messenger filters), but infantile. I would describe the proposed solution as a place of man + product, rather than man + visual modification of man. This is intended to imply an image of greater maturity, professionalism and brand awareness. In practice, it is meant to be a place where existing brands can sell products right away. The product focus is also meant to clearly differentiate this solution from the filters familiar from TikTok/Instagram, or animated emoticons on iOS.
Clothing in Metaverse
Just how fresh and hot the topic of digital clothing, and the entire emerging market associated with it is, is indicated by the huge interest generated by the Connect 2021 conference, during which the CEO of Facebook, or, for some, META, presented the Metaverse (’meta’- beyond, and 'universum’- world). This is the concept of a new internet combining the 'internet of things’ with the 'internet of people’. Mark Zuckerberg explained in an interview with The Verge that the Metaverse is „an embodied internet where instead of just viewing content – you are in it”. The author of the term itself is Neal Stephenson, who used it nearly thirty years ago in his cyberpunk book Snow Crash. In it, he describes the story of people living simultaneously in two realities – real and virtual.
The question is not „will it happen?” but rather „when and how it will happen?” As augmented, and virtual reality technologies become increasingly present in our lives, the world that now surrounds us on a daily basis will migrate into the Metaverse. Offices, pubs, gyms, flats are all now our mundane lives and will also be present in digital life. At the center, however, will always be people and their experiences. But what would interactions with others be like without the right attire? A „burning” t-shirt of your favorite band at a virtual concert; a waterfall dress during a New Year’s Eve meta-ball, or a golden shirt at a business meeting summarizing a successful project – although it sounds like science-fiction, this series of articles is an attempt to respond to such needs.

Gif.3. Digital clothing in Metaverse
Conclusion
The evolution of the e-commerce market towards Digital Fashion has already begun. This is possible thanks to the dynamic development of technologies such as Pose Estimation, 3D graphics, and hundreds of other smaller, but very important, innovations appearing every day. In this article, we’ve given an overview of what digital clothing is and the opportunities it presents – for software developers on the one hand, and designers and graphic designers on the other.
In the future articles we will focus on technical issues related to the created application and market. Those interested can count on a large dose of code in Python associated with Pose Estimation and Blender 3D. There will also be plenty of news related to Digital Fashion and Metaverse.
All content in this blog is created exclusively by technical experts specializing in Data Consulting, Data Insight, Data Engineering, and Data Science. Our aim is purely educational, providing valuable insights without marketing intent.


 (+48) 508 425 378
(+48) 508 425 378 office@bitpeak.pl
office@bitpeak.pl